Mounts
Maksutov Cassegrain Telescopes
General properties of Maksutov-Cassegrain Telescopes
Maksutov-Cassegrain is a sealed tube telescope very similar to the Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope. Maksutov-Cassegrain uses a thicker corrector plate than the Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope.
Design of Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope. (Available from:http://www.vikdhillon.staff.shef.ac.uk/teaching/phy217/telescopes/phy217_tel_catadioptric.html. [accessed 29 Oct, 2019] )
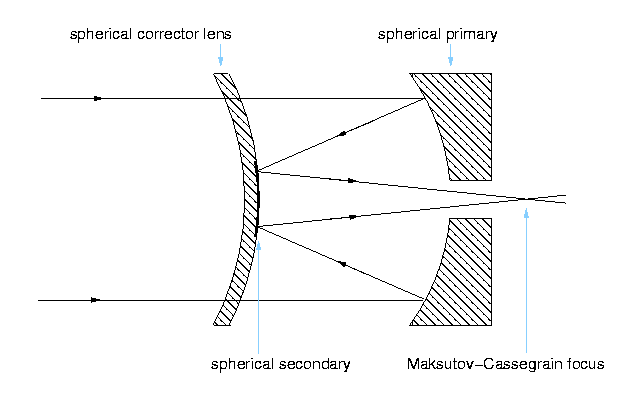
Path of the light in Maksutov-Cassegrain Telescope
-
Light enters the tube through the corrector lens and is then reflected from the primary mirror which is located at the other end of the telescope.
-
Once reflected, the light travels to the secondary mirror. The secondary mirror is an aluminated plate in the center of the corrector plate.
-
From there, it passes through a small hole in the primary mirror to the eyepiece.
Observations with Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope
Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope is quite small in size, which gives it proper resolution and high contrast — great for planetary observing.
Because of a small secondary mirror obstruction, the image is very sharp.
With the focal ratio between f11 and f15, the field of view is rather narrow - meaning that the "deep-space" objects appear very small in the field. Although Maksutov-Cassegrain is small in size, it is quite heavy (heavy corrector lens).
A short presentation of the Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope type is available here.
Slideshare presentation of Maksutov-Cassegrain telescope
Short Presentation | Maksutov-Cassegrain Telescope | Optics Trade from Optics-Trade
Filters
Sort
Filters
Sort